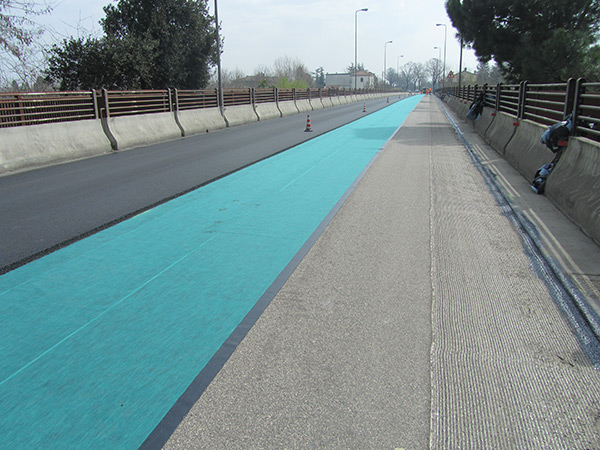

Road Diaphragm
GRID BIT is a road diaphragm, a real form of reinforcement that distributes weight of roads with high volume of heavy-duty traffic and thereby increases fatigue resistance while greatly reducing stress.
The road diaphragm GRID BIT can extend the life-span of roads and in many cases, it represents a much more cost-effective alternative to the complete overhaul of deteriorated roads.
the different problems GridBit can solve

-
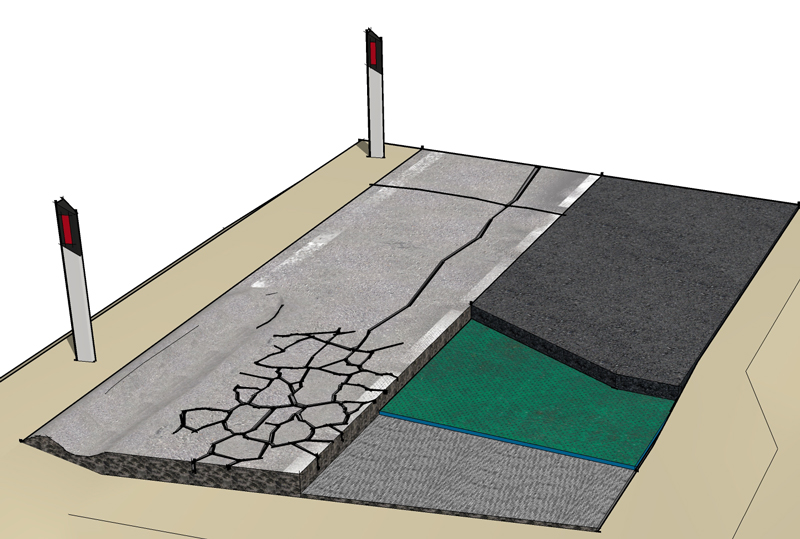
RUTTING
Rutting, i.e. the plastic deformation of the surface layers with the formation of channels which may also depend on the temperature or the reduced bearing capacity of the substrate due to traffic loads.
GRID BIT DS helps to apportion loads better in order to better distribute them on the substrate.
The interconnection between the new and old roadbed is fundamental.See the technical data sheet
Close -
Close
ANTI PUMPING
On roads with cracks, the passage of vehicular traffic after poor weather conditions such as rain or snow applies pressure to the first unbound road layers with the consequent upwards rising of fine materials and water.
This then generates cavities that accelerate the increase of stresses, causing a decrease in bearing capacity and the consequent degradation of the superstructure up to the formation of holes.
The particular architecture of GRID BIT DS ensures total waterproofing on unbound layers, foundations and substrates, preventing the phenomena of pumping and the rise of fine materials, reducing or eliminating the effects of degradation on the road’s surface layer.See the technical data sheet
-
CRACKS
The layers connected to the base of a road are subjected to tensile phenomena, as an effect of the road surface’s inflection due to the passage of motor vehicles and/or heavy loads.
These tensile forces are lower than the material’s tensile strength, but the cyclical nature of the stress induces decreased tensile strength and brings about microfractures, gradually larger and larger, that rise to the top.
GRID BIT DS, laid in relation to the degree of deterioration above or below the binder layer, acts as a shield that prevents cracking from spreading to overlying layers.See the technical data sheet
Close
